Voluntary Carbon Market Insights & FAQs
Everything you’ve ever wanted to know about the voluntary carbon market – and more!
CORSIA
What is CORSIA?
CORSIA stands for the Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation. It is a global scheme designed to address CO2 emissions from international aviation. CORSIA is the first global market-based measure for any sector.
What is the goal of CORSIA?
CORSIA aims to reduce emissions from international aviation in a harmonised way that minimises market distortion. It achieves this by offsetting the CO2 emissions that cannot be reduced through technological advancements, operational improvements, and sustainable aviation fuels.
How does CORSIA work?
What are the phases of CORSIA?
- Pilot phase: 2021-2023 (voluntary participation)
- First phase: 2024-2026 (voluntary participation)
- Second phase: 2027-2035 (mandatory participation based on states’ RTK levels in 2018, with some exceptions)
Who participates in CORSIA?
Participation in CORSIA is voluntary from 2021 to 2026. After 2026, participation becomes mandatory for most states, with some exceptions. As of 2024, 126 countries are participating in CORSIA, covering 64% of 2022 airline emissions. Airlines flying between these participating states must comply with CORSIA’s offsetting requirements.
What are CORSIA Eligible Units?
EEUs are carbon credits that meet specific criteria set by ICAO, the International Civil Aviation Organization. These criteria relate to the carbon crediting program, methodology used, and vintage range (years of emissions reductions). To be fully eligible for the First phase, credits must also receive a Letter of Authorization (LoA) from the host country where the emissions reductions occurred, confirming the intention for corresponding adjustments.
Why is there concern about the availability of EEUs?
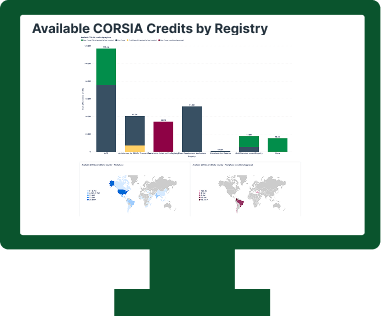
The supply of EEUs for the First phase in its early stages remained very limited. As of October 2024, only 7 million fully authorised First phase credits are available, originating from an ART project in Guyana.
Millions of credits from other registries are eligible under ICAO’s criteria but have not received LoAs from their host countries, making them ineligible for the First phase. The limited supply raises concerns about whether CORSIA will function effectively as a market instrument.
Current CORSIA First Phase Supply
Main Challenges:
- The slow pace of LoA issuance by host countries.
- Uncertainty around the processes and criteria for granting LoAs (Authorization).
- Limited capacity in some countries to assess and authorize emissions units (overselling risk).
Potential Solutions:
- Increased clarity and communication from ICAO to states and airlines on CORSIA requirements.
- Streamlining LoA processes and providing capacity-building support to states.
- More active participation from airlines in supporting the carbon market to stimulate supply.