
Voluntary Carbon Market Insights & FAQs
Everything you’ve ever wanted to know about the voluntary carbon market – and more!
Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE)
What Role Does Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) Play in Carbon Dioxide Removal?
- Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) is a carbon removal approach that adds alkaline substances to seawater to accelerate the ocean’s natural carbon sink. This process converts dissolved CO2 in seawater into stable bicarbonates and carbonates, which can store carbon for around 10,000 years.
- By creating a CO2 deficit in surface waters, OAE draws additional CO2 from the atmosphere to restore balance. While this alkalinity boost happens naturally over geologic timescales through rock weathering, it can be greatly accelerated by adding alkaline materials such as olivine, basalt, or carbonates to beaches or the open ocean.
Why Is Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) Important for Climate and Ocean Health?
- Permanent carbon storage – Converts CO2 into stable bicarbonate and carbonate ions, storing carbon for thousands of years.
- Ocean health – Raises seawater pH, helping to counteract ocean acidification and protect marine ecosystems.
- Scalability – Leverages the ocean as the largest natural carbon sink on Earth, offering vast removal potential.
What Is the Current Market Activity for Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) in Carbon Removal?
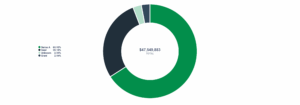
- The Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) market is still in its early stages but is gaining momentum. To date, 150,000 credits have been purchased through offtake agreements. Investment in the sector has reached approximately $47 million, indicating growing confidence in its potential for large-scale, durable CO2 removal.
- Credit prices for OAE range from $400 to $1,500 per ton, making them the most expensive carbon removal credits currently available. This premium reflects both the technology’s emerging status and its promise for long-term permanence.
Total investment by round
What Is the Current Project Activity and Capacity Development in Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) Worldwide?
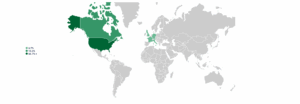
- Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) projects are emerging across multiple regions, with the largest share of developers based in the United States. Other active countries include France, Germany, Italy, and the United Kingdom, each hosting a smaller but notable share of global activity.
- Although the sector is still in its early stages, developer participation is expanding as more pilot projects are launched. The strong presence in the US, combined with growing engagement from European countries, reflects increasing global interest in OAE and its potential as a scalable, durable carbon removal solution.
Share by country – CDR developers
How Does AlliedOffsets Track Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) Credit Activity in the Voluntary Carbon Market?
AlliedOffsets tracks OAE credit activity in the voluntary carbon market (VCM) using data from 35+ registries, providing the most comprehensive dataset available. Our coverage includes:
- OAE issuances
- Retirements
- Offtake agreements
- Purchase vs. delivery trends over time
Quarterly prices
Who Is Purchasing Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) Credits?
- The Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) market, while still in its early stages, is being driven primarily by a small group of influential buyers. Frontier stands out as the biggest advocate for this technology, having purchased the majority of OAE credits issued so far. British Airways follows as another significant buyer, contributing to early demand and helping to build credibility for the sector.
- As a relatively new CDR type, OAE is still establishing its commercial track record.
CDR purchases by buyer sector

What Are the Main Challenges in Scaling Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE)?
The main challenges in scaling Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) stem from cost, complexity, and uncertainty, including:
- High deployment costs – Offshore logistics and infrastructure are expensive.
- Verification difficulty – Measuring and attributing CO2 uptake accurately is complex.
- Ecosystem risk – Uncertain impacts on marine ecosystems from pH changes.
- Public acceptance – Concerns over altering marine chemistry.
- Regulatory gaps – No clear governance for large-scale open-ocean interventions.
What Are the Key Benefits of Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) for Carbon Removal and Marine Ecosystems?
The key benefits of Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) highlight its ability to deliver durable carbon removal while supporting ocean health and ecosystems, including:
- Permanent carbon removal – Stores CO2 as stable bicarbonates for millennia.
- Ocean health – Raises pH, helping reverse acidification impacts.
- Large-scale potential – Oceans cover 70% of Earth’s surface.
- Natural process – Builds on natural alkalinity buffering.
- Co-benefits – Supports biodiversity and coastal resilience.
- Circular economy – Can use industrial waste streams such as brine or slag.