
Voluntary Carbon Market Insights & FAQs
Everything you’ve ever wanted to know about the voluntary carbon market – and more!
Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS)
What Is Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) and How Does It Work?
- Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) is the process of capturing and permanently storing CO2 emissions generated from using biomass (organic matter) for energy production.
- BECCS is projected to remove 0.5-2 GtCO2 per annum by 2050 according to the IPCC’S best estimate
- Types of BECCS:
- BECCS Power – Uses bioenergy power plants to generate electricity while capturing CO2 emissions from biomass combustion.
- BECCS Industry – Integrates carbon capture into industrial processes (e.g., cement or steel) where bioenergy is the fuel source.
- BECCS Hydrogen – Produces hydrogen from biomass gasification or fermentation, capturing CO2 during conversion.
- BECCS Energy-from-Waste (EfW) – Captures CO2 from waste-to-energy plants using biomass or organic waste feedstock.
Why Is Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) Important in Tackling Climate Change?
- Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) is a key technology in the fight against climate change because it offers scalable negative emissions, making it one of the most promising options for this decade. It captures and stores CO2 in geological formations for centuries, ensuring long-term removal from the atmosphere.
- Experts view BECCS as critical to achieving long-term Net Zero goals, especially in hard-to-abate sectors where other mitigation options are limited. Beyond carbon removal, BECCS can also generate renewable electricity, hydrogen, or industrial heat: delivering both clean energy and permanent sequestration.
How Active Is the Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) Market and What Does It Mean for Carbon Removal?
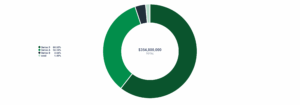
- 2025 has been the strongest year yet for BECCS, reflecting growing demand and confidence in the technology’s role in delivering large-scale, durable carbon removals. The sector has also attracted substantial financial backing, with $354 million invested to date.
Total investment by round
What Is the Current Project Activity for Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) Worldwide?
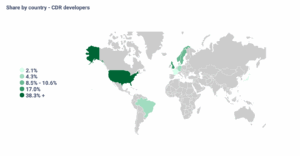
- The current project activity for Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) is led by around 47 active developers worldwide. The sector is the leading engineered carbon removal (CDR) type in terms of credit issuances, with over 23 million credits issued to date. Prices typically range between $300–500 per ton. This technology has been gaining increased attention in recent years, driven in part by the involvement and advocacy of multiple industry associations, which are helping to accelerate adoption and investment.
- The top suppliers in the space include Atmosclear, Stockholm Exergi, and Ørsted, with most of the supply coming from Denmark, the United States, and Sweden.
How Are Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) Credits Issued, Retired, and Traded in the Voluntary Carbon Market?
BECCS credits are issued, retired, and traded in the voluntary carbon market (VCM) through registry activity that AlliedOffsets tracks in detail. With data from 35+ registries, we provide the most comprehensive credit tracking available, covering:
- BECCS issuances
- Retirements
- Offtake agreements
- Purchase vs. delivery trends over time.
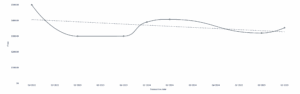
Quarterly prices
Who Is Purchasing Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) Credits and What Are the Market Trends?
The Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) market is currently dominated by a small number of major buyers, with Microsoft having purchased roughly 90% of all credits issued to date. Other key purchasers include entities from Denmark and Frontier, which together account for much of the remaining contracted volume.
CDR purchases by buyer sector

What Are the Biggest Challenges to Scaling Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS)?
The biggest challenges to scaling Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) are:
- High costs – Setup and maintenance are capital-intensive.
- Biomass supply – Requires sustainable, reliable feedstock sourcing.
- Logistics – Transporting biomass and CO2 can be costly.
- Land and water use – Can compete with food production and ecosystems.
- Social acceptance – Public resistance to large-scale infrastructure.
What Are the Advantages of Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) for Net Zero Goals?
The main advantages of Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) for Net Zero goals are:
- Carbon-negative energy – Removes CO2 while producing usable energy.
- Long-term storage – Geological sequestration ensures permanence.
- Circular economy – Converts waste biomass into energy and negative emissions.
- Mature technology – Commercial-scale plants already operating.
- Essential for Net Zero – Addresses emissions from hard-to-abate sectors.